Researchers Min-Hao Hung, Kuo-Chuan Lin, Chung-Cheng Wu, Jia-Hung Juang, Yen-Yu Lin, and Chi-Yao Chang published an article titled “Effects of Complex Functional Strength Training on Balance and Shooting Performance of Rifle Shooters” in the Applied Sciences Magazine in 2021.
The objective of the study was to investigate the effects of complex functional strength training, involving whole-body vibration and unstable surface training, on overall shooting performance. This included assessing the shooters’ stability of hold, time on target, and body sway.
Let us delve into this article and explore important strategies that can enhance your shooting skills.
The research aimed to assess how whole-body vibration (WBV) combined with unstable surface training (UST) affects the performance of shooters. Eight athletes from the Taiwan National Air Rifle Team participated, meeting specific criteria to minimize external influences. Ethical guidelines were strictly followed, with approval from the Ethics Committee of Fu Jen Catholic University Institutional Review Board, and informed consent was obtained from all participants.
The experimental design involved a six-week study comparing UST intervention among shooters on a vibration training platform, analyzing differences in shooting performance, shooting muzzle kinematics, and static balance. Participants underwent two separate tests in a shooting range, with a minimum 48-hour interval to mitigate fatigue and potential neuromuscular effects. Precautions were taken regarding diet and test timing to ensure consistency among participants.
During the study sessions, specific shooting and center of pressure tests were conducted, utilizing standardized equipment and procedures. Participants were subjected to shooting simulations conforming to international standards, with data collected on 60 shots per session. Static balance tests were performed, with center of pressure changes recorded. Training involved a structured regimen including warm-up exercises on a treadmill, followed by UST on an unstable surface using a BOSU balance trainer. Researchers ensured consistent foot positioning and safety measures throughout the training and testing phases.
The study found significant improvements in shooting scores and trajectory values after a 6-week WBV+UST intervention compared to pretest performances. A one-way RM ANOVA revealed a notable increase in shooting scores (F = 23.730, p < 0.01, power = 0.985) and a decrease in total time (F = 5.909, p < 0.05, power = 0.553) post-intervention. Specifically, shooting scores improved by 6.25% after the 6-week intervention period. Trajectory values also showed improvement, with significant differences observed in 10–50 ms-DevTotal and 10–50 ms-DevY categories, indicating enhanced shooting performance and stability. Post-hoc analysis further confirmed the effectiveness of the 6-week WBV+UST intervention in improving shooting performance relative to pretest conditions.
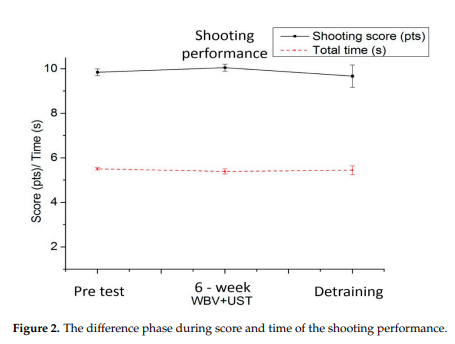
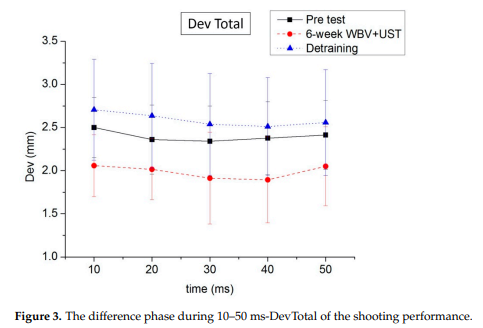
This study underscores the crucial role of stability in gun-holding for achieving superior shooting proficiency. The improvement in DevTotal values, particularly the enhanced posture control stability 10 ms prior to firing resulting from training, highlights the significance of maintaining stability for indirect performance enhancement. Previous research corroborates these findings, suggesting stability maintenance should be prioritized in training programs for both novice and elite athletes.
This seems to be the first study investigating the impact of WBV+UST on professional sports proficiency and balance. The use of UST on a vibration platform appears to be an effective method for enhancing lower limb stability. While previous studies have shown improvements in lower limb muscle activation with similar oscillations, the absence of electromyography (EMG) in our study limits detailed conclusions on muscle activation.
The observed reduction in total time during shooting indicates improved fluency and potentially reduced fatigue among players. Proper timing has been linked to enhanced shooting performance, emphasizing the importance of timing for firing fluency and score improvement. Overall, the WBV+UST method shows promise in enhancing shooting performance, with significant improvements noted in stability, fluency, and scores.
These findings have implications beyond shooting sports, extending to activities requiring stability maintenance such as archery, gymnastics, and ballet. However, further studies are needed to determine the optimal settings for WBV+UST and to address limitations such as small sample size. Biomechanical assessments and prospective long-term studies are recommended to provide deeper insights into the efficacy of WBV+UST in improving athletic performance.
Hung, M. H., Lin, K. C., Wu, C. C., Juang, J. H., Lin, Y. Y., & Chang, C. Y. (2021). Effects of complex functional strength training on balance and shooting performance of rifle shooters. Applied sciences, 11(13), 6143.




